
$ docker exec bash -c "command1 command2 command3" In order to execute multiple commands using the “docker exec” command, execute “docker exec” with the “bash” process and use the “-c” option to read the command as a string. Great, you are now able to run commands as the root user within a container with docker exec. $ docker exec -u 0 įor example, in order to make sure that we execute the command as root, let’s have a command that prints the user currently logged in the container. In order to execute a command as root on a container, use the “docker exec” command and specify the “-u” with a value of 0 for the root user. In some cases, you are interested in running commands in your container as the root user. If you don’t specify the “IT” option, Bash will still get executed in the container but you won’t be able to submit commands to it. In order to get the results from your command, you are also binding the standard output and the standard error to the ones from your host machine.Īs you are binding the standard input from your host to the standard input of your container, you are running the command “interactively”. When running “ docker exec” with the “-i” option, you are binding the standard input of your host to the standard input of the process you are running in the container. So how are file descriptors related to the “ docker exec“?
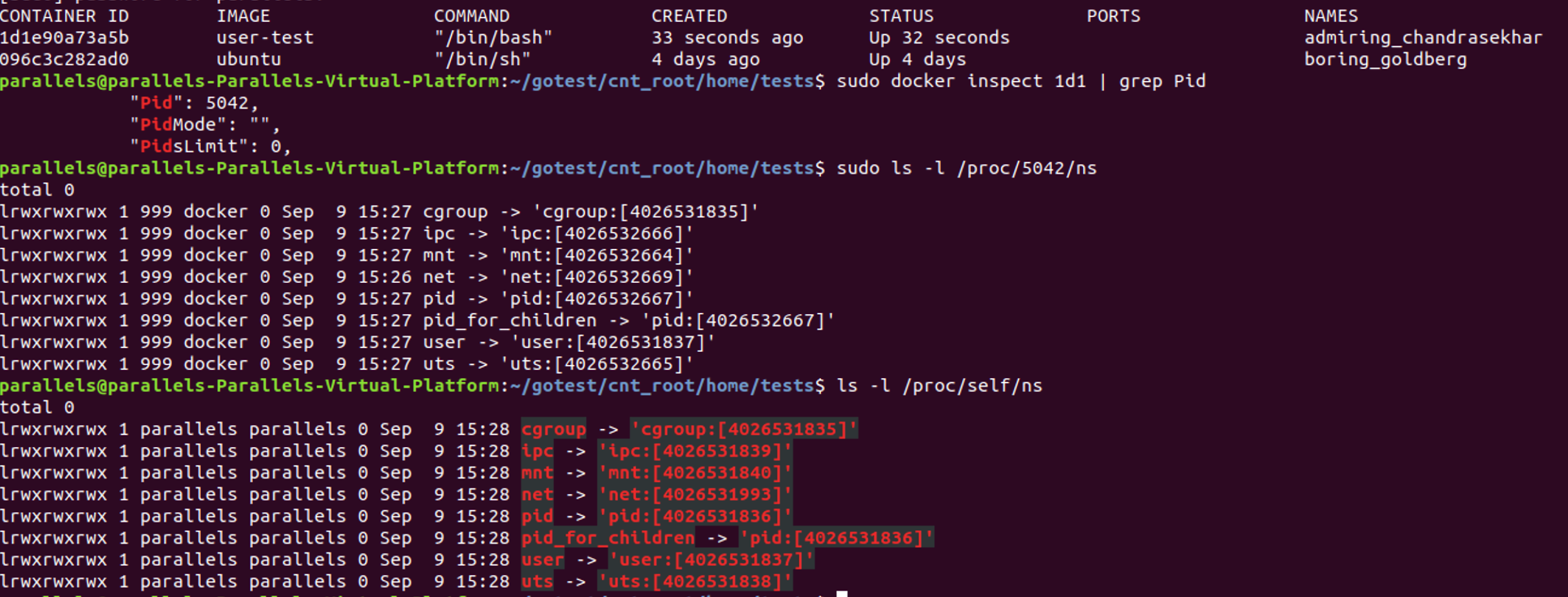
Note : the “docker ps” is also used in order to determine whether a container is running or not.Īs you can see, the container ID is the first column of the ‘docker ps’ output. $ docker psĬONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUSħ4f86665f0fd ubuntu:18.04 "/bin/bash" 49 seconds ago Up 48 seconds

In order to determine the container name or ID, you can simply execute the “docker ps” command. The first thing that you need to do is to identify the container name (if you gave your container one) or the container ID. $ docker exec Īs an example, let’s say that you want to execute the “ls” command on one of your containers. In order to execute commands on running containers, you have to execute “docker exec” and specify the container name (or ID) as well as the command to be executed on this container. Executing a command in a specific directory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
